PicoBuck – RGB LED Driver
- Ethan Zonca
- http://www.protofusion.org
- 15.027 Views
- easy
- Tested
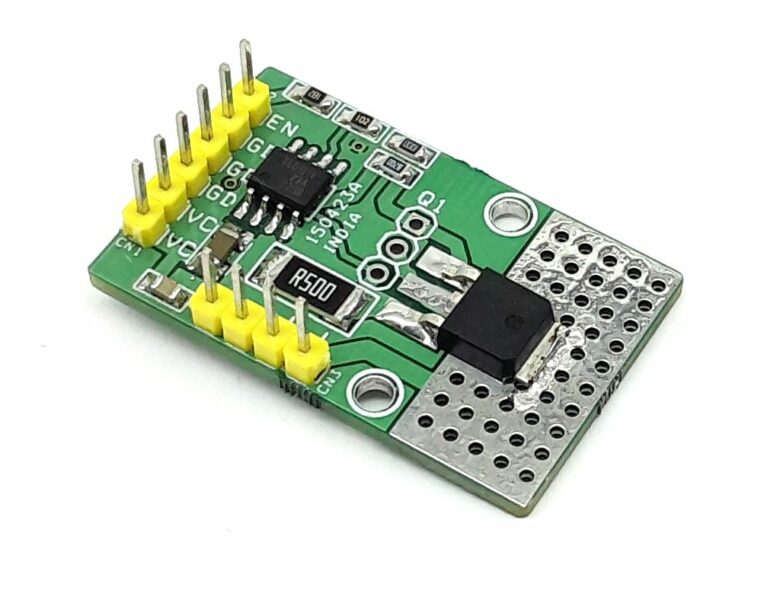
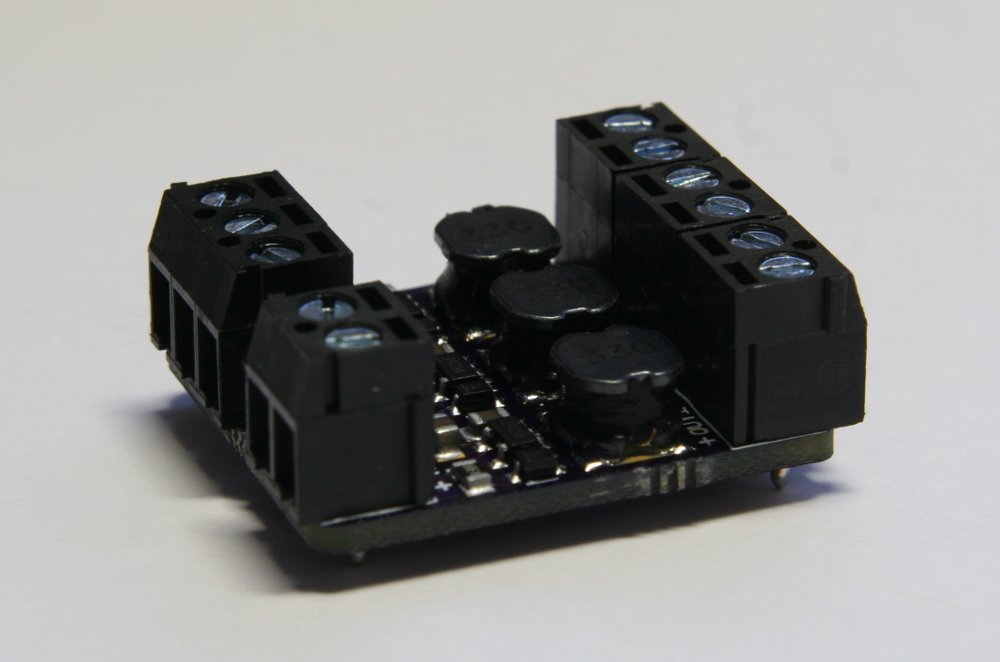
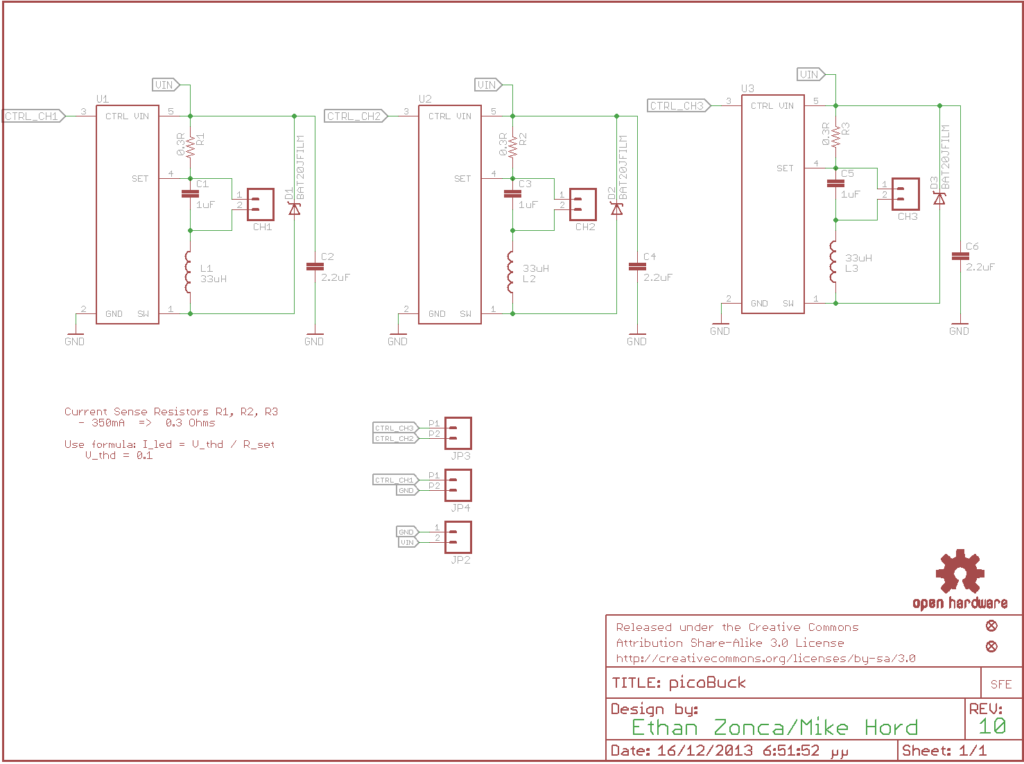
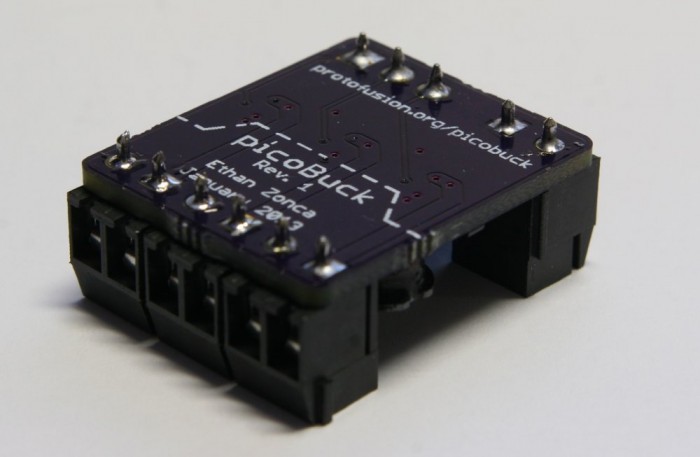
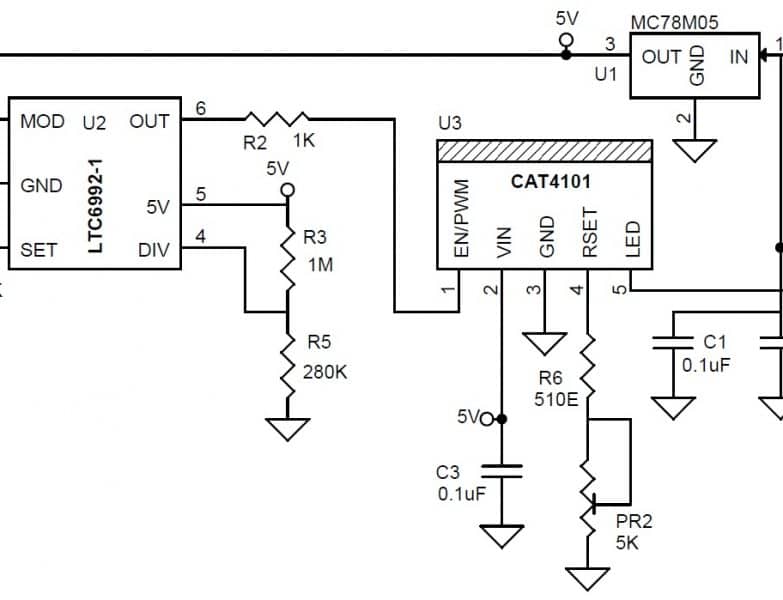
The PicoBuck is a small and inexpensive 3-channel LED driver. It employs constant-current buck driving which approaches an efficiency of 95% (theoretical). It’s based on AL8805 LED Lighting Buck Driver from Diodes Inc.
Description
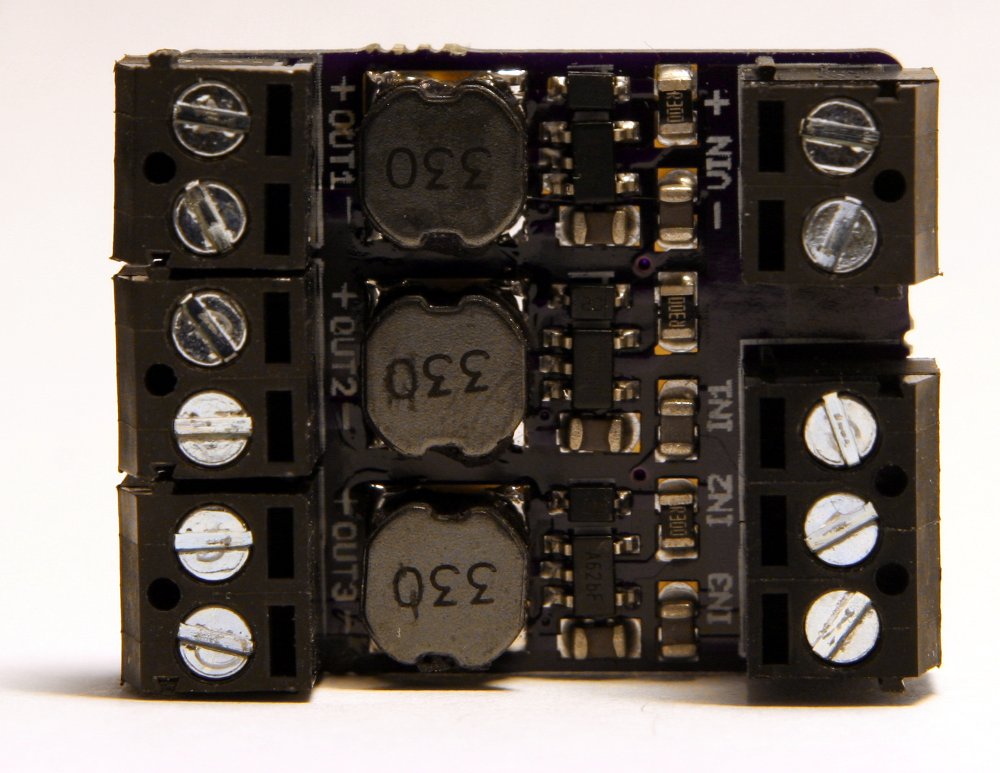
The PicoBuck supports a wide range of input voltages (6v to 20v) which may be connected to the VIN header. It has three inputs for each driver channel, labeled IN1, IN2, and IN3 which may be driven with standard 3.3v or 5v logic. LEDs are connected to the outputs of the driver, OUT1 through OUT3. Each channel of an RGB LED must be connected to the driver separately: this driver, like most buck drivers, does not support common-anode or common-cathode RGB LEDs.
Each channel of the PicoBuck can drive an LED at 350mA on the standard model. The driving current is set by a small current sensing resistor populated on the board. If you need to drive LEDs at higher or lower currents, just swap out the current sensing resistor to achieve your desired current. You can calculate the value of your current sensing resistor with the AL8805 spreadsheet.
Usage
Digital Mode
To use digital drive mode, apply a standard 3.3v or 5v PWM signal to any of the 3 inputs. This method gives good brightness resolution over the entire range of brightness when using 8 to 10 bit PWM.
Analog Mode
To use analog mode, apply an analog voltage between 0v and 2.5v to any of the 3 inputs. This analog voltage controls how much current the LED is driven at, up to the current set by the current-limiting resistor. Note that the analog method is not effective for the last 20% of currentat this point, the current drops to zero.
Alternatively, you may employ a compound approach using analog dimming for high brightness and PWM dimming for low brightness. This method achieves optimal brightness resolution with minimal flicker, but is more challenging to implement in software.